ANDRITZ HYDRO’s history of pumped storage technology in Asia
Since the very beginnings of pumped storage technology, ANDRITZ has continued to provide groundbreaking technology. Having delivered about 500 pumped storage units with a total capacity of about 40,000 MW worldwide, the company has been involved in many major projects around the globe. Highlights include Vianden in Luxembourg, the largest pumped storage plant in Europe, and Goldisthal, the largest in Germany and the first with variable speed outside Japan. Northfield and Castaic in the USA, Edolo in Italy, Malta-Reisseck in Austria, Drakensberg in South Africa and Aldeávila in Spain are other key ANDRITZ references.
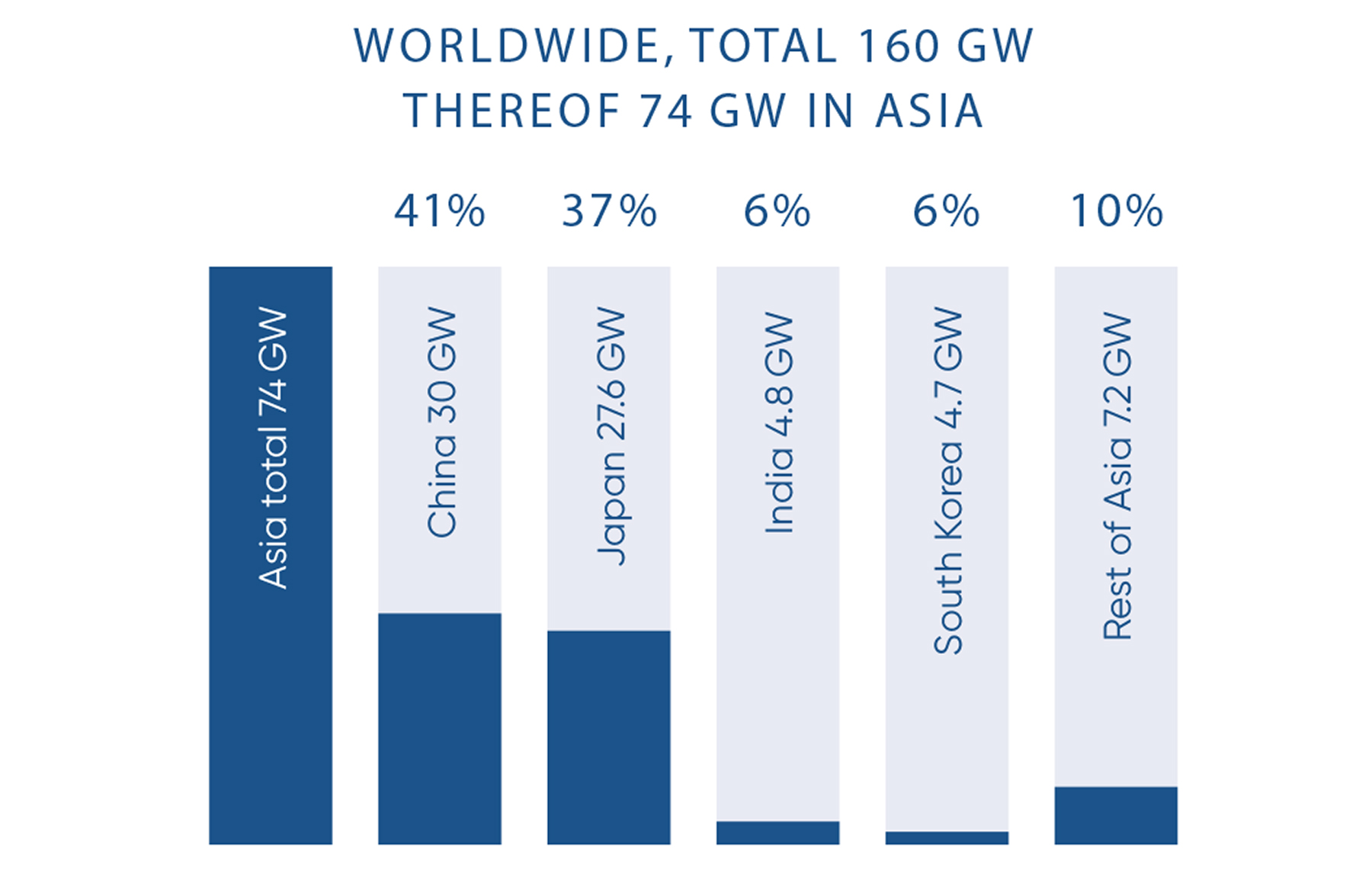
In Asia, ANDRITZ was the supplier for several pumped storage plants, such as Tianhuangping,Shi San Ling, Lang Ya Shan, and Tongbai in China. Currently, the company is executing a contract for two asynchronous generating units for Feng Ning II in China, which will become the largest pumped storage plant in the world when completed.
Pumped storage is a proven, highly efficient and low-risk technology. It benefits from long asset lifetimes and demonstrates lower operating costs than any other bulk power storage technology currently available. By successfully integrating intermittent renewable generation resources into the grid, pumped storage hydro can thus contribute significantly to a clean energy future.