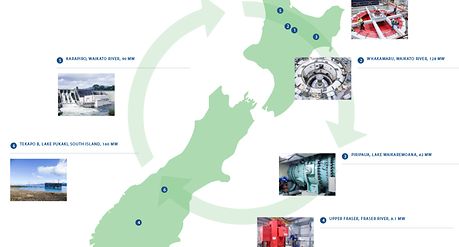
The two main islands are interconnected for electrical distribution by high voltage DC cables. Two thirds of the population live in the North Island, which is the main source of electricity demand, but electricity can be transferred in both directions depending on the hydrological situation.
New Zealand has committed to be 100% renewable by 2035 and the trend towards replacing fossil fuels and industrial heat with renewables is expected to lead to a doubling of electricity demand by 2050.
This poses a significant challenge for the development of new generation capacity. New Zealand’s installed hydropower capacity of 5,437 MW is entirely conventional hydropower, with no pumped storage. Most of the hydropower plants in New Zealand were installed between the 1940s and 1980s. As a result, the bulk of recent capacity growth has been the refurbishment of existing hydropower plants along with the installation of smaller run-of-river schemes. With lower environmental impact, run-of-river schemes and small storage schemes continue to be the favored option for new hydro capacity in New Zealand. Consequently, uprating and refurbishment of existing hydro plants will also likely continue in the medium term.
In order to reach the ambitious national goals for renewable energy, much of the new capacity development will be focused on geothermal and wind energy. Nonetheless, such developments will require the higher performance, flexibility and reliability available from traditional sources of generation like hydropower to perform vital grid control and peaking power functions.